Click on the link below to read the post at it’s original source location on Substack.AND support this creator’s important work! $8 a month; $40 a year.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurological condition that can affect how a person communicates, interacts with others, and experiences the world. The term “spectrum” reflects the wide variation in characteristics and support needs among individuals with autism.
An autistic person may process sensory information differently. They may have heightened or reduced sensitivity to various stimuli, such as smells, lights, or sounds, and may exhibit different communication skills, often preferring routine and predictability.
ASD is an umbrella term that includes a range of neurodevelopmental features. Autism is not a disease, but it can have a significant impact on a person’s life.
Its effects can vary widely. Some people will need lifelong support, while others can live and work independently.
In some cases, the features of the condition may be present from infancy. In others, the signs may become more obvious as the individual becomes older.
Parents or caregivers may notice that a young child:
- does not babble by the age of 12 months or produce words by 16 months
- does not respond when people talk to them but reacts to other sounds
- does not make eye contact
- lines up toys or objects excessively
- does not want to be cuddled
- does not play with others or play make-believe games
Link: Learn more about the signs of autism in a 3-year-old.
An older child may:
- have difficulty starting conversations
- have difficulty making friends and interacting with others
- use repetitive or atypical language
- be uncomfortable with changes to their routine
- be extremely passionate about specific topics or objects
Virtual Autism
In 2018, Marius Zamfir, a Romanian psychologist, used the term “virtual autism” to describe behavioral abnormalities seen in children between birth and three years old, arising from sensory-motor and socio-affective deprivation caused by exposure to more than four hours/day of virtual environment.
Unlike Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), virtual autism is thought to be environmentally induced, specifically by prolonged exposure to television, tablets, smartphones, and other digital devices.
Other risk factors that contribute to incidences of virtual autism among babies, toddlers, and older children include:
- Reduced physical activities cause an imbalance in a child’s sensory experiences, putting them at a higher risk of developing virtual autism.
- The lack of opportunities for young children to engage in real-life human interactions with others prevents the development of social skills that are needed to form and maintain reciprocal relationships.
The condition typically affects children under 3, when brain development is most active and susceptible to environmental influences. During this critical period, real-world interactions are essential for developing communication skills, emotional regulation, and social understanding.
Virtual Autism Symptoms
Virtual autism symptoms refer to behaviors and challenges that appear in online or digital environments, similar to real world autism traits. People may struggle with social interactions in virtual spaces, misinterpret online cues like emojis or tone, prefer structured digital routines, or intensely focus on specific online interests.
Some of these behaviors can resemble high functioning autism symptoms, such as social withdrawal, strong focus on certain interests, or reduced engagement with others.
Common Virtual Autism Symptoms Include :
- Delayed speech development
- Limited eye contact
- Lack of social engagement
- Repetitive movements or behaviors
- Short attention span
- Hyperactivity and/or impulsive behaviors that interfere with a toddler’s learning.
- Difficulty paying attention or inability to focus on the task at hand.
- Decreased cognitive ability
- Frequent frustration, irritability, or mood swings in real-world situations.
- Speech delay in toddlers due to insufficient social interactions in real life. A toddler who was speaking at first may also stop talking after developing virtual autism.
- Isolation or social disconnection.
- Loss of interest in activities they enjoyed previously. Instead, the child may be more comfortable with the smartphone, TV, or computer.
- Repetitive movements or autism tics, such as hand flapping, finger flicking, or rocking
Key Differences Between Virtual Autism and Real Autism
While the symptoms of virtual and real autism may look similar on the surface, there are clear differences:
- Cause: Virtual autism is triggered by prolonged screen exposure, while real autism is linked to neurological and genetic factors.
- Reversibility: In virtual autism, symptoms often improve once screens are removed and healthy routines are established. Real autism symptoms persist over time and require ongoing therapy.
- Development History: Children with virtual autism may have developed normally until screens became a major part of their environment. In contrast, real autism often shows signs much earlier, regardless of screen use.
- Response to Interaction: Children with virtual autism generally respond better to face-to-face interactions once screens are limited. Children with real autism may struggle with communication and social cues, even in screen-free settings.
The Psychology Of Excessive Screen Time
In the same way that physiologically to a large extent we are what we eat, psychologically to a large extent we are what information we consume.
The graphic below displays the dramatic effect of a congenital deficiency of just one essential nutrient, Iodine.

Let’s examine the media created and broadcast by media companies.
Why are we moving towards extremely ‘simple’ information?
The brain uses a lot of energy.
Typically when an individual is given the choice of a difficult task or an easy task they will choose the easy task. When there’s an option the brain goes for the task that is simpler, which uses the least amount of energy.
Thus the media created has become increasingly simplified. The competition for consumers information attention has resulted in the growth of primitive content. This process has escalated over time. And we are the content that we consume.
We used to be a civilization of texts and systemic thinking and we are transitioning to a civilization of visual images. No analytical thinking and no systemic thinking.
The Neurophysiological Effects
How do these structural changes in the information we consume effect our neurophysiology of thinking?
Recent research into how the working brain operates has revealed new information about how it works.
As the graphic shows below, the thinking apparatus of the brain uses three basic modes or systems.
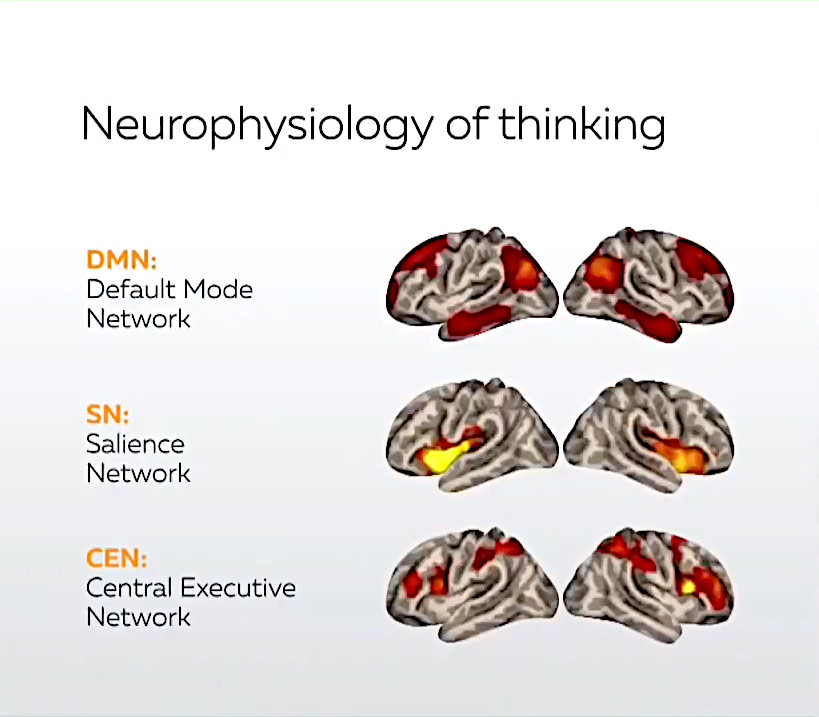
The bottom line illustrates the ‘Central Executive Network’ which is the information collection aspect of the brain.
The middle line is the ‘Salience Network’ which is the aspect of the brain that is used for getting its bearings, state of being or situation.
The top line is the ‘Default Mode Network’ which is the ‘Hot Brain’, the ‘Fiery Brain’ or ‘Systemic Thinking Brain’. This is the aspect of the brain that doesn’t just think about something in particular. A prime example of the functioning of this is when someone asks you what you’re thinking and you realize you’re thinking about this and that, and respond by saying “Nothing in particular”.
This is the most important mode for operation of the brain because your brain is running the various game scenarios and is thinking systemically, and this is the time that you’re getting the most important insights and solutions. This can lead to what’s commonly known as an ‘aha!’ moment.
Brain scientists use to think that the brain is organized locally, with zones in the brain that have different functions such as the visual cortex, the auditory cortex, motion cortex. But recently the brain has been found to be much more complicated.
During the first twenty five years of life, the neurons outside of the brain connect with those inside the brain. This creates the neuro-networks. These networks are responsible for the three modes of operation described above.
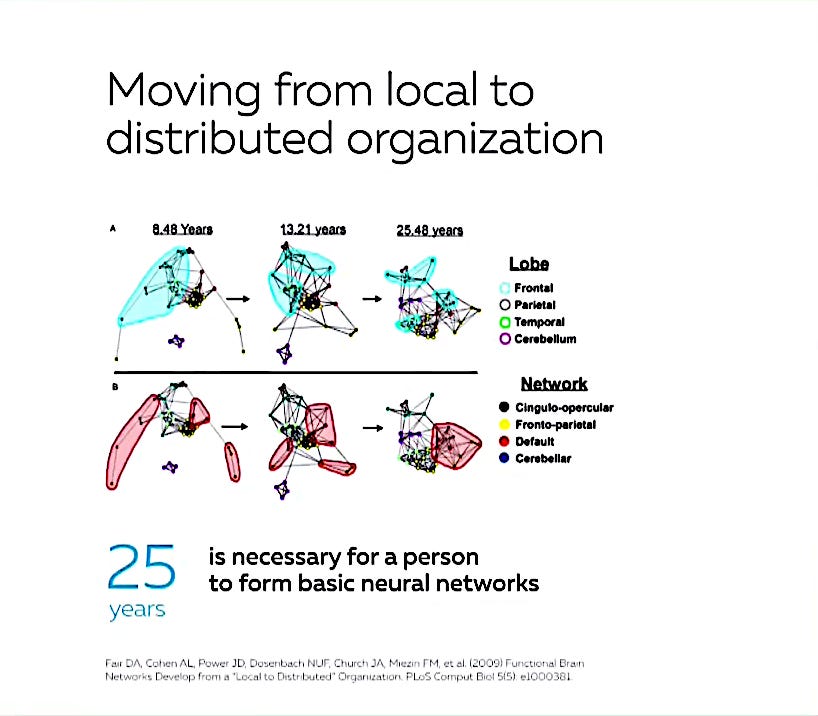
Connections in the brain are initially local and for us to concentrate and get our bearings in various situations takes 25 years.
What develops over these years is the creation of a programmed server, that will be responsible for thinking as an adult. During the first 25 years of life every human is essentially programming or hard wiring and coding their brain.
So what is the current situation that the youth are in when they are hard coding their brain in the current hyper-information environment?
How does that affect their thinking?
The most unpleasant thing is that their default mode network gets suppressed.
Research has determined that the three networks or modes of the brain, described above, are antagonistic. If the Executive Network and the Salience Network are activated they suppress the Default Mode Network. Conversely, when the Executive Network and the Salience Network are depressed, the Default Network is activated.
When content is consumed continuously and your Executive Network is continuously active and that means your ‘Default Mode Network/Systemic thinking Brain’ is getting no energy causing it to, in effect, go into hibernation.
So it should not be surprising that when people shift from Twitter or Facebook over to an Instagram or TikTok thinking template, that they don’t develop. And this is what happens with adults as well.
What about the children?
In the U.S. and Russia 40% of the children under 10 years of age are online nearly all of the time they’re awake to consume information and some of those leave their devices on while they sleep to respond to calls or messages.
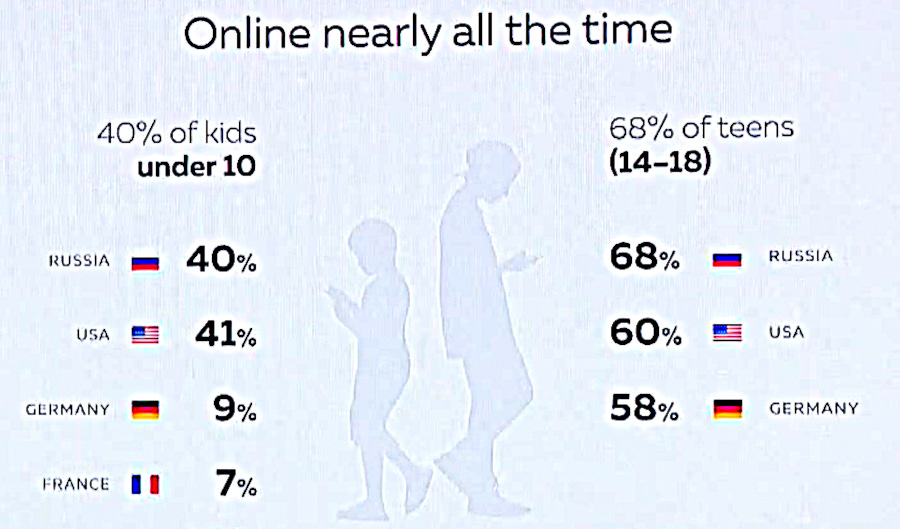
By the age of 14 most of the children in the world that have access to the internet spend 60 to 70% of their time on line.
So they put their ‘Systemic Thinking Network’ into hibernation mode. But this isn’t the only problem. To shift your brain out of hibernation mode and back into ‘Systemic Thinking Mode’ takes around 23 minutes.
In 2016 studies show that the average user was shown to be interrupted roughly every 15 minutes, so they rarely would allow 23 minutes to pass in order to reactivate their ‘Systemic Thinking Network’. These statistics have only gotten worse over the last 9 years.
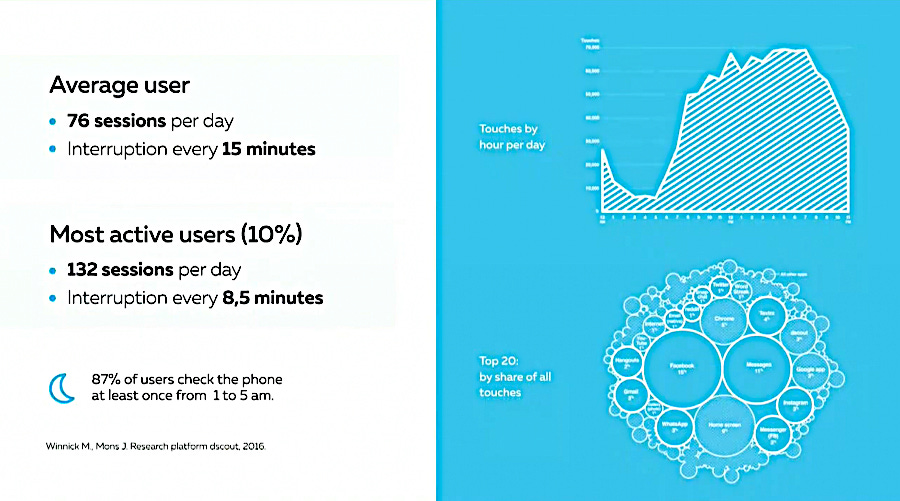
In addition to the above issues there is the fact that the ‘Default Mode Network/Systemic thinking Brain’ is crucial for the development of social interaction skills. If this network is not functioning due to its suppression by the ‘Executive Network’ then the social interaction skills are not developed properly.
In 1997 the amount of screen time that users spent was equal to the amount they spent physically interacting with other people. In 2007, with the arrival of the IPhone, screen time was in excess of 8 hours with face to face time under 2 hours.
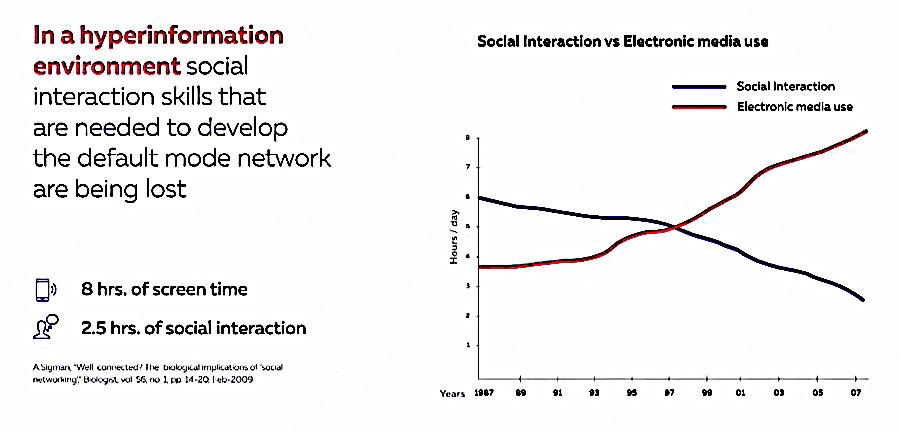
The net result of the combined effects of this technology is that we have an epidemic of what’s become known as Digital Autism.
‘Digital Autism’ is described as a condition where children cannot sustain a long term psychological contact with each other. They’re not interested in the other person’s internal world. Other people are easily replaceable for them. They don’t see any value in these relationships. Even when on a date with someone, they may prefer their smart phone to face time with their date.

Research done in 2018, in which researchers used a large selection of individuals, showed that if smart phone users spent more than 2 1/2 or 3 hours using their phone the self injury behavior and depressive disorders increase dramatically.
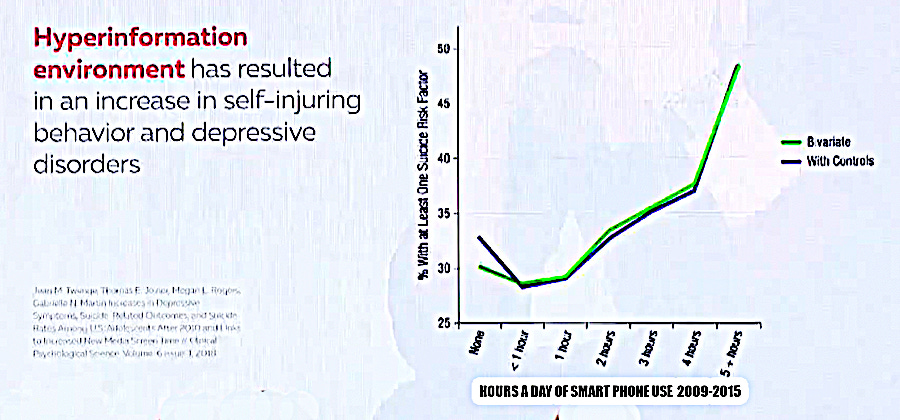
The peak of the graph above is showing the increase of self-injuring behavior and depressive disorders.
Some people try to remove the depressive disorders by using the phone, but for the majority of people the use of the phone leads to social anxiety and other disturbances.
Social networks are to blame here.
Researchers in Israel did a comparison between those who use phones and those who don’t. Believe it or not there are some who don’t.
In this case people who hadn’t been using smart phones were asked to use them for 3 months and as a result their social alertness and anxiety increased along with aggression and internal animosity.
The Distal Vision Phenomenon

Our goals are critical to the extent to which our brain can look into the future to forecast and think about our future.
If the ‘Default Mode Network/Systemic Thinking Brain’ in not working due to hyper-information overload, the ability to look into the future is lost. So the person cannot be motivated and create goals.
In another research project, several hundred people divided into three groups were challenged by creative and thinking tests. The three groups were separated with all of their smart phones turned off, while one group was required to leave their smart phone in another room, one group had their phone in their pocket or their bags and one group had their phone in front of them on their desk, screen down.
The physical presence of a phone influenced the level of the operational memory, the random access memory and the fluid intelligence.
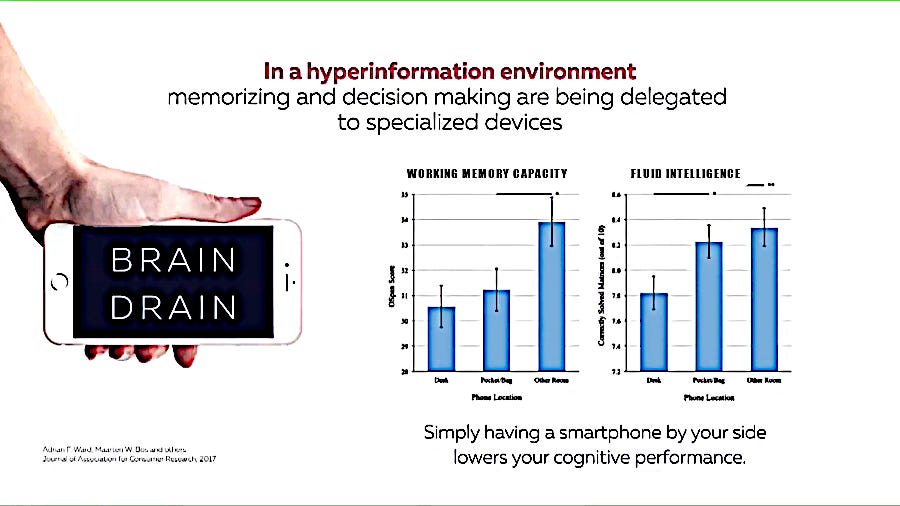
The shortest column shows the levels with the phone on the desk and the tallest column shows the phone in another room. So the Working Memory and the Intelligence both increase when the phone is completely removed from their immediate location. When individuals have a phone on or near them their memory and intelligence tend to decrease.
Digital Autism Is Not Just For Young Children and Young Adults
The milder forms of Classic Autism overlap the symptoms of Digital Autism making it challenging to determine whether the root cause is physiological and/or psychological for these behaviors and effects.
With the recent massive increase in mild forms of autism among children and younger adults it is safe to assume that the primary cause is the addictive use of Smart Phones, predominantly, along with pads, laptops and desktop computers.
Many people who, for years, compensated in various ways for their tendency to be autistic, have exhibited mild Digital Autism symptoms since they became addicted to Smart Phones. Do you know anyone like this?
Many children who grew up planted in front of the TVs starring at cartoons and children’s shows all day, have ended up being adults with symptoms of Digital Autism that only got worse once they became addicted to computer screens and Smart Phones.
At this point Digital Autism has become epidemic with an ever increasing number of adults of all ages exhibiting the symptoms, with the primary one being the loss of interest and ability to communicate with others face to face.

Here’s the kicker…..This is all by design as part of the construction of the the Panopticon that’s being constructed. Full Spectrum Surveillance. Divide and Conquer. The Smart Phone is the main tool created by the parasites to completely divide, track, target, indoctrinate and control the population.
Using Cell Phones Isn’t Smart
If You Want To Be Healthy And Free

Recommend Terra Times to your readers
Dedicated To Understanding The Simple, Final Truth.
One thought on “There’s An Epidemic of Digital Autism”